The IEX India index stands for the Indian Energy Exchange.
What is IEX?
The Indian Energy Exchange, or the IEX, is a marketplace for electronic power trading for all the electricity corporations and boards for trading contracts related to energy.
In a nutshell, just like how individuals trade in the stock market to earn a profit, electricity corporations can trade on the IEX to increase their profitability and have better price discovery.
The exchange was founded in 2008 and has its headquarters in New Delhi, India.
This exchange provides a place for the participants where they can buy and sell energy through the double-sided closed auction process.
The exchange is regulated by the Central Electricity Regulation Commission, which in turn regulates the IEX, just like how SEBI regulates the NSE and BSE.
Markets offered by IEX:
IEX offers trading choices in three different types of markets.
The following are the three different types of markets that IEX allows for trading:
#1.) Electricity Market:
Electricity markets allow trading in the various market sectors.
The following are the various market sectors that the electricity market provides:

#1.) Day-Ahead Market:
Day-Ahead Market (DAM) is a physical electricity trading market for deliveries for some or all of the 15-minute time blocks within the next 24 hours from midnight.
Here, the prices and the quantum of the electricity to be traded are determined through a double-sided closed auction bidding process.
The following are the features of DAM trading:
- Double-sided anonymous auction bidding process.
- Trading of the 15-minute contracts.
- Clearance is obtained from the SLDC by the buyers as well as the sellers based on the availability of the network and the ABT meters as well.
- Risk management is through the requisite margin.
- Congestion management is done through market splitting and also by determining the Area Clearing Price (ACP) specific to any area.
#2.) Term Ahead Market:
Term Ahead Market (TAM) will provide a range of products that will allow the participants to buy or sell electricity on a term basis for a duration of up to 11 days ahead.
Currently, the products included in this market are intra-day, term-ahead contracts, and day-ahead contingency, which will help the participants to manage their electricity portfolio for all the different durations.
The following are the features of TAM trading:
- Firm delivery because the contracts under the TAM can be used to ensure the delivery of electricity a few days in advance.
- It is also the trading of the region’s specific contracts.
- There are the following types of delivery blocks:
- FBA: firm foundation: 24 hours
- FDY: firm day: 11 hours.
- FNT: firm night time: 8 hours
- FPK: firm peak time: 5 hours
- Risk management is through the collection of margins as specified in the bye-laws, rules, and other regulations of the exchange.
#3.) Real-Time Market:
The real-time market (RTM) is a very new market segment where trading commenced on June 1, 2020.
Here, the price and quantum of the trade are determined through the double-sided closed auction bidding process.
The following are the main features of RTM trading:
- It has a double-sided auction bidding process.
- Trading is of the 15 minutes contracts.
- It allows the exchange to publish the area clearing price (ACP) and the area clearing volume (ACV).
- The buyers and the sellers will obtain clearance from SLDC based on the availability of the network and the ABT meters.
- The exchange allows managing risk through leveraging the bank balance, and requisite margin, including any additional margin as specified for the respective trading segment.
#4.) Cross-border Electricity Trade:
The Cross Border Electricity Trade (CBET) commenced after the trade with Nepal through DAM on April 17, 2021.
This will encourage the expansion of the Indian power market towards building an integrated South Asian power market.
The DAM and TAM enabled the grid connection with South Asian countries like Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
The following are the main features of CBET:
- It has a very integrated power market.
- It has also got competitive power prices.
- It is transparent and has efficient power procurement.
- It allows resource optimization.
- It also has enhanced energy access as well as security.
#2.) Green-Market:
Just like the electricity market, the green market also has two different sectors.
They are as follows:

#1.) Green term ahead market:
The Green Term Ahead Market (G-TAM) is a very new market segment for trading in renewable energy.
The new market segment will feature contracts such as Green Intraday, Green Day Ahead Contingency (DAC), Green Weekly, and Green Daily.
The matching mechanism for green intraday, green DAC, and green daily is continuous or spot trading, whereas the matching mechanism for green weekly is the double-sided open auction process.
The following are the main features of the green-term ahead market:
- All the contracts here are at the national level.
- The exchange allows managing risk through leveraging the bank balance, and requisite margin, including any additional margin as specified for the respective trading segment.
- Trading is for the 15- minute time block in G- intraday, G-DAC, whereas there is the trading of certain blocks for G- daily and weekly.
- It is a market mechanism to facilitate the achievement of national renewable energy capacity addition as well as effective integration of green energy in the country.
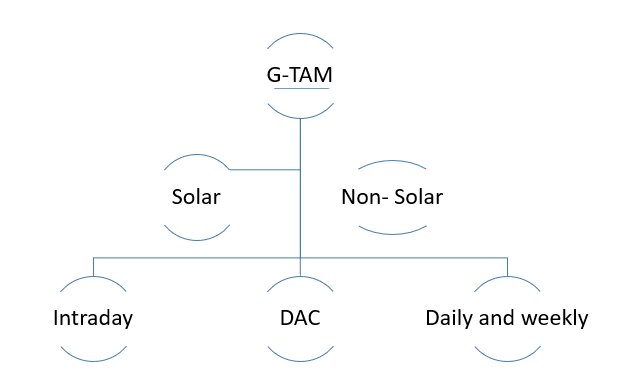
#2.) Green day ahead market:
The same will commence on October 26th, 2021, and will allow anonymous and double-sided closed collective auctions in renewable energy on the day ahead.
The exchange will invite bids for conventional and renewable energy in the most integrated way through separate bidding windows.
The following are the key features of the green market for the day ahead:
- It provides the bid categories for buyers and sellers of solar, non-solar, and hydro.
- It provides the trading of the 15-minute contract.
- The exchange allows managing risk through leveraging the bank balance, and requisite margin, including any additional margin as specified for the respective trading segment.
- It has a separate formation for green and conventional power.
- It has a separate quantity limit for the sellers in each category.
- The participants can either use a premium or discount price at the time of placing their bid.
- It is also a double-sided anonymous closed bidding auction.
- It has a separate price structure for green and conventional power.
- The buyers and sellers are asked to submit the NOC from their respective SLDC based on the availability of the network.
#3.) Certificates:
The certificate market also provides two types of certificates.
They are as follows:

#1.) Renewable Energy Certificates:
This allows the easy purchase of renewable energy by the state utilities as well as the obligated entities, including the states that do not have RE sources.
One REC represents 1 MWh of energy that is generated from renewable sources.
The following are the main features of the same:
- It is valid for 1095 days after issuance.
- Banking as well as the borrowing segment is not allowed.
- It also allows a single transfer.
- You can trade on the power exchange platform only.
#2.) Energy Savings Certificates:
This scheme covers 478 designated consumers from 8 different energy-intensive sectors.
The sector-wise distribution is as follows:
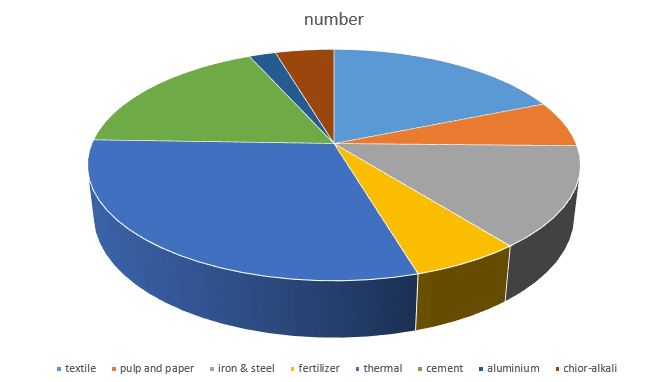
The following are the main features of the same:
- It has a compliance period of 3 years.
- Banking is also allowed for 2 consecutive cycles.
- Buyers and sellers can sometimes exceed their goals.
- The entire phase cycle is for 3 years.
- The target entity has designated customers.
Who can trade on IEX?
The IEX isn’t a good place for all retail investors.
An individual can trade on the exchange provided they own an establishment that will require tons and loads of power.
Apart from this, the individual will also require the necessary clearance from the CERC to be able to trade on the platform.
To be able to trade on this platform, the member or the client should have the capital of at least RS. 150 lakhs.
Conclusion:
We hope that the above blog about the IEX has helped you to gain a good level of knowledge and understanding of the same.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
About Us:
Trading Fuel is our blog website where we provide you with the basics of finance, economics, the stock market, and advanced technical analysis tips. Stay tuned with us for more of these glorious blogs.

